Table of Content
- Understanding Fibonacci Retracement
- How to Use Fibonacci Retracement?
- Trading Using Fibonacci Retracement
- Fibonacci Retracement with Additional Indicators
- Determining Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels
- Role of Fibonacci Retracement in Trading Decisions
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Advanced Techniques
- Conclusion
Fibonacci retracement is a technical analysis tool that is widely applied by traders to mark out possible levels of support and resistance in the financial markets. The method draws on the Fibonacci sequence, which is a sequence of figures where a number is the addition of the two preceding numbers.
Though the sequence itself is of natural and mathematical importance, its use in trading originates from the ratios which are extracted from it, to estimate potential price action.
Having knowledge of Fibonacci retracement and utilising it in an effective way may assist traders in identifying possible areas for decision-making, depending on market conditions and strategy. It may be more effective in highly trending markets, enabling the trader to set up potential levels of entry and exit.
The following article covers Fibonacci retracement, explaining what it is, how to use it, and how to apply it together with other indicators in order to produce a more efficient trading strategy.
However, it should be noted that no technical analysis tool guarantees success, and market conditions may impact the effectiveness of Fibonacci retracement.
Understanding Fibonacci Retracement
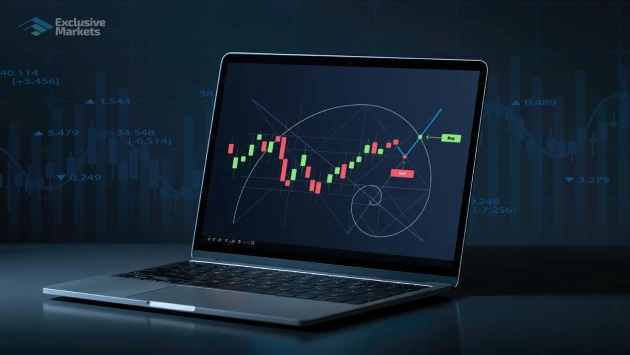
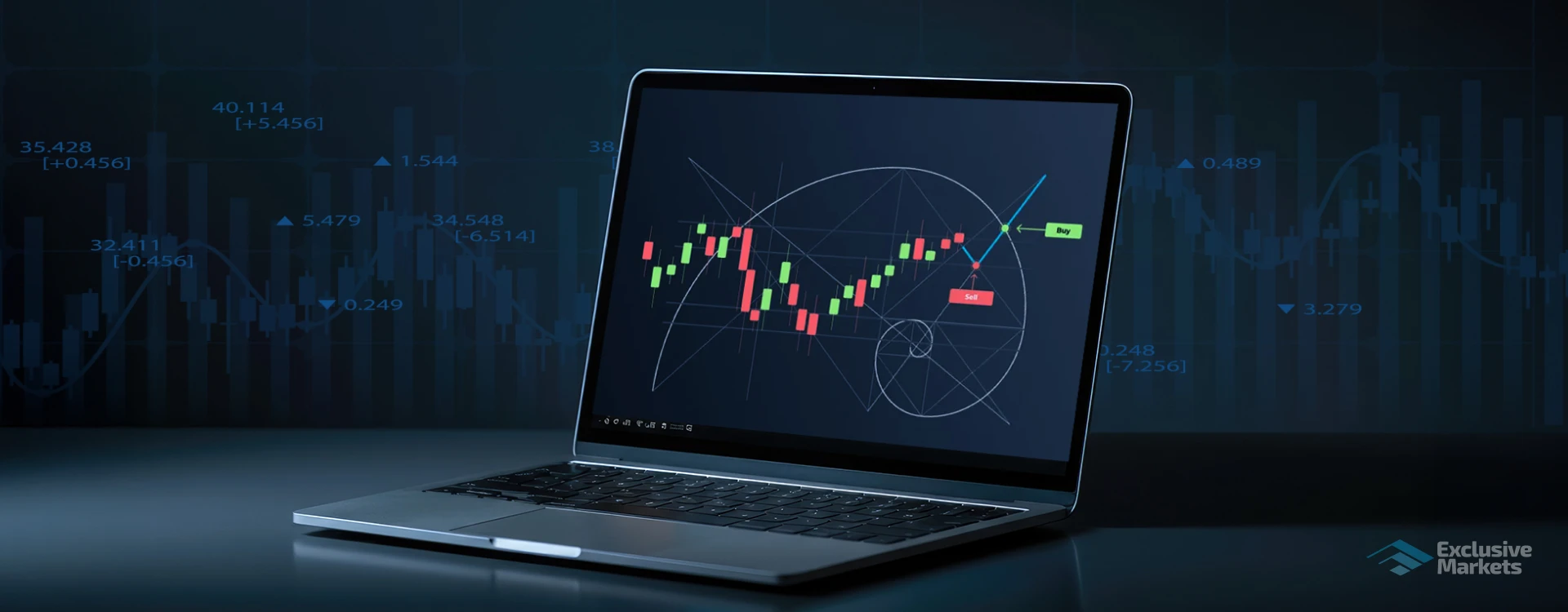
Fibonacci retracement levels are derived from the major Fibonacci ratios: 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 78.6%. These percentages indicate what portion of the prior move the price might retrace before potentially continuing in the direction of the original trend. While the 50% level is not actually a Fibonacci number, it is added because of its long-standing presence in market corrections.
These Fibonacci retracement levels are also possible regions of support or resistance where price reversals are likely to occur. When a financial instrument makes a strong move up or down, it never moves in a straight line. Instead, prices tend to recoil before resuming their trend, and Fibonacci retracement suggests possible areas where such recoil could stop.
How to Use Fibonacci Retracement?
Applying Fibonacci retracement entails determining a major price movement, whether an uptrend or a downtrend, and then using the retracement tool to determine the possible levels at which price corrections may stop.
For an uptrend: Click on the lowest price level (swing low) and draw the Fibonacci retracement tool to the highest price level (swing high). The levels obtained will indicate potential support levels where the price might find buying interest and continue its upward trend.
For a downtrend: Begin at the highest price level (swing high) and pull down to the lowest price level (swing low). The Fibonacci levels in this case may act as resistance, indicating where selling pressure could increase before the price resumes its decline.
Upon usage, the Fibonacci retracement levels are shown as horizontal lines on the chart, offering traders a visual guide of potential reversal points.
Trading Using Fibonacci Retracement
The achievement of Fibonacci retracement tool depends on the reaction of the price to these levels. Traders normally wait for confirmation signals to enter a trade.
- Uptrend Support: If the price retreats to a Fibonacci level such as 38.2% or 61.8% and then turns around, this could indicate the continuation of the uptrend. Traders may consider this as a potential buying opportunity.
- Downtrend Resistance:When the price retraces to a level of Fibonacci and then begins descending again, it may indicate that the downtrend continues. Some traders might view this as a selling opportunity.
Relying solely on Fibonacci retracement indicator is not advisable. Other confirmations need to be observed, like candlestick patterns, volume analysis, and trend strength indicators.
Fibonacci Retracement with Additional Indicators
In order to improve reliability, Fibonacci retracement is often used in combination with other indicators. Some of the most popular tools employed are:
- Moving Averages: When a moving average intersects at a Fibonacci level, it may help confirm the existence of that level.
- Trend Lines: In case a trend line coincides with a level of Fibonacci retracement, chances of price turning around may increase.
- Candlestick Patterns: There is confirmation whenever there is formation of hammers, engulfing candles, or doji candles at Fibonacci levels.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): When RSI shows overbought or oversold conditions around a Fibonacci level, it could confirm probable reversals.
With the integration of these indicators, traders are able to screen out false signals and make more informed trading decisions.
Determining Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels
Risk management is extremely important when it comes to trading, and Fibonacci retracement can assist traders in estimating stop-loss and take-profit levels accordingly.
- Stop-Loss Placement: Where a long entry is made at the 61.8% retracement, a stop-loss may be set below the 78.6% level to reduce risk.
- Take-Profit Targets: Extension levels of Fibonacci, for instance, 127.2% and 161.8%, can help traders define potential exit levels based on historical patterns, though this does not guarantee any specific return.
Applying Fibonacci retracement in risk management should be part of a broader strategy that considers overall market conditions.
Exclusive Markets provides traders with advanced charting tools and a seamless trading experience, making it easier to apply tools effectively in real-time market conditions.
Role of Fibonacci Retracement in Trading Decisions
Fibonacci retracement is a valuable tool for traders, helping to identify potential price reversal and continuation areas by analysing historical price movements. It allows traders to anticipate market behaviour during price swings, as pullbacks often occur when traders take profits.
By pinpointing retracement levels, traders can make informed entry or exit decisions within trends, such as identifying buying opportunities in an uptrend or recognising selling pressure in a downtrend.
This structured approach may support more disciplined decision-making by identifying strategic price levels, but outcomes depend on multiple market factors.
While effective, Fibonacci retracement should not be used in isolation, as market dynamics are influenced by various factors. Combining it with other technical tools like moving averages and support zones enhances analysis and validates potential reversal points.
Additionally, it aids in risk management by allowing traders to set well-defined stop-loss and take-profit levels based on these retracement levels. By using Fibonacci retracement across different timeframes, traders can adapt their strategies to both short-term and long-term trends, leading to more disciplined and confident decision-making.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While Fibonacci retracement is a useful tool, it's often misused by traders who minimise its value. These are some of the pitfalls to avoid:
- Using Fibonacci Alone: Always use it along with other tools.
- Using Fibonacci on Small Timeframes: It is generally more reliable on larger timeframes such as the daily or four-hourly charts.
- Ignoring the Overall Trend in the Market: Strong trends can dominate Fibonacci levels.
- Not Waiting for Confirmation: Traders should wait for price action signals before making a decision.
As traders are aware of these errors, they become better at applying Fibonacci retracement and make better decisions.
Advanced Techniques
Professional traders utilise Fibonacci retracement in combination with Fibonacci extensions to forecast price targets.
- Fibonacci Clusters: When there are several Fibonacci levels from various timeframes which come together at roughly the same price level, this makes the level more significant.
- Theory of Elliott Wave: Fibonacci retracement is applied by most traders to quantify correcting waves and Fibonacci extensions to forecast impulsive wave targets.
Such sophisticated methods further enhance trading strategies and validate trade setups further.
Conclusion
Fibonacci retracement is a useful tool for determining financial market key support and resistance levels. Though it is not fail-safe, coupling it with other technical analysis indicators, risk management, and an effective trading plan can support better-informed decisions when used as part of a comprehensive strategy.
Traders who are adept with Fibonacci retracement can employ it to enhance trade entries, exits, and profitability. If its principles are comprehended and one does not make common pitfalls, traders may improve their decision-making in the financial markets.
Explore your trading strategies with the advanced charting tools and support available at Exclusive Markets, while staying aware of trading risks and get access to a wide range of assets, competitive trading conditions, and exclusive support.
Are you Ready to Explore the World of Trading?
Disclaimer: The information provided on this blog is for educational/informational purposes only and should not be considered financial/investment advice. Trading carries a high level of risk, and you should only trade with capital you can afford to lose. Past performance is not indicative of future results. We do not guarantee the accuracy or completeness of the information presented, and we disclaim all liability for any losses incurred from reliance on this content.
 1794
1794 25-08-2025
25-08-2025